The theme of this year’s World Diabetes Day is “Diabetes across the life course”. WHO: Number of people with diabetes has more than quadrupled in three decades Healthcare
November 14 is World Diabetes Day, with this year’s theme being “Diabetes in the Life Course.” The World Health Organization emphasizes that the disease affects people of all ages and requires constant attention throughout life.
Increase in incidence
According to WHO, the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise rapidly, especially in low- and middle-income countries. From 1990 to 2022, the number of people living with diabetes increased from 200 million to 830 million. In 2022, 14 percent of people over the age of 18 had diabetes, up seven percent from 1990. However, more than half (59 percent) of adults over 30 years of age diagnosed were not taking medications to control the disease. The lowest treatment coverage is recorded in low- and middle-income countries.
Complications of the disease
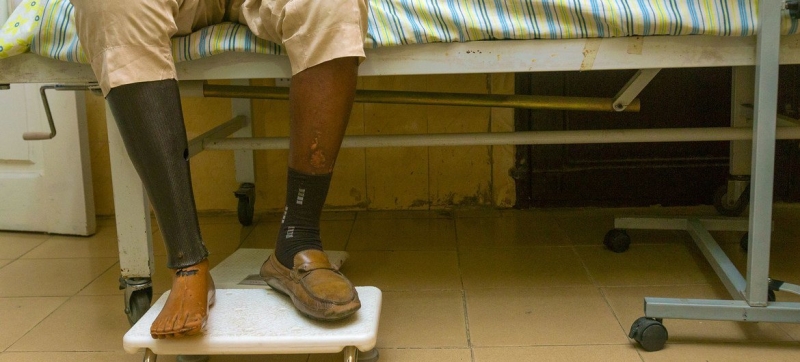
Diabetes remains a leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks and strokes, and often leads to lower limb amputations. Diabetes was the direct cause of 1.6 million deaths in 2021, with 47 percent of these deaths occurring in people under 70 years of age. Another 530,000 deaths were attributed to kidney disease caused by diabetes. Elevated blood sugar is responsible for about 11 percent of deaths from cardiovascular disease. In total, over two million people are estimated to have died from diabetes and related complications in 2021.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes develops either because there is insufficient insulin production or because the body cannot use it effectively. Prolonged hyperglycemia leads to damage to blood vessels and the nervous system. Symptoms may appear suddenly, but with type 2 diabetes they are often mild, leading to late diagnosis and complications. Type 2 diabetes accounts for more than 95 percent of all cases, and is increasingly being diagnosed in children.
Treatment and prevention
WHO emphasizes that prevention of type 2 diabetes is possible. A healthy diet, regular physical activity, maintaining a normal body weight and quitting smoking can help prevent or delay the development of the disease. Early diagnosis and regular health screenings remain key to preventing severe consequences.
The organization reminds you that diabetes is manageable. A combination of diet, exercise, medication, and treatment of complications helps slow the progression of the disease. WHO continues to support countries in strengthening prevention and care systems, including implementing the Global Pact to End Diabetes and achieving global care coverage targets by 2030.
